Overview:
A set in Python represents the mathematical concept of sets. Python provides two types of set implementations: A set and a frozenset. Sets are mutable sequences. A value can be added to a set containing the values {"Red", "Green"} and the set grows into {"Red", "Green", "Blue"}.
The frozenset is also a set, however a frozenset is immutable. Once a frozenset is created, new elements cannot be added to it. A frozenset with value {128, 150, 175} once created, cannot be added with new elements. The elements of a frozenset object cannot change their values.
Hashable Property of frozenset:
A frozenset is hashable, meaning every time a frozenset instance is hashed, the same hash value is returned. The hashable property of the frozenset makes it qualified to be a key in a Python dictionary. The hashable property of the frozenset also makes two frozenset objects to be compared for equality.
Creating frozenset objects in Python:
The constructor of a frozenset takes an iterable object and returns a frozenset instance. In case if no iterable object is passed, the constructor returns an empty frozenset. In both the cases the returned frozenset is immutable.
Applications of frozensets:
Applications of frozensets include set of sets and dictionaries where the keys are required to be pairs or triples.
Frozenset operations:
Since frozenset objects are immutable, the following set methods are not supported by frozenset: update(), intersection_update(), symmetric_difference_update() ,add(), remove(), discard(), pop(), clear(). The following set operators are also not allowed on a frozenset object: |=, &=, -=, ^=.
Example 1:
|
# Sample Python program for frozenset singleDigitPrimes = (2,3,5,7)
# Single digit prime numbers as a Python frozenset singleDigitPrimeSet = frozenset(singleDigitPrimes)
# Prime numbers less than ten as a Python frozenset primeLTTen = frozenset((2,3,5,7))
# Prime numbers less than twenty as a Python frozenset primeLTTwenty = frozenset((2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19))
# Check the single digit prime number set # and the prime number set less than ten are same print("Single digit prime number set is equal to prime number set of numbers less than the integer ten:%s"%(primeLTTen == singleDigitPrimeSet))
# Check the single digit prime number set # and the prime number set less than twenty are same print("Single digit prime number set is equal to prime number set of numbers less than the integer twenty:%s"%(primeLTTwenty == singleDigitPrimeSet))
# Are the prime numbers less than ten and the prime numbers less than twenty are disjoint print("Prime numbers less than ten and the prime numbers less than twenty are disjoint:%s"%(primeLTTen.isdisjoint(primeLTTwenty))) |
Output:
|
Single digit prime number set is equal to prime number set of numbers less than the integer ten:True Single digit prime number set is equal to prime number set of numbers less than the integer twenty:False Prime numbers less than ten and the prime numbers less than twenty are disjoint:False |
Example 2:
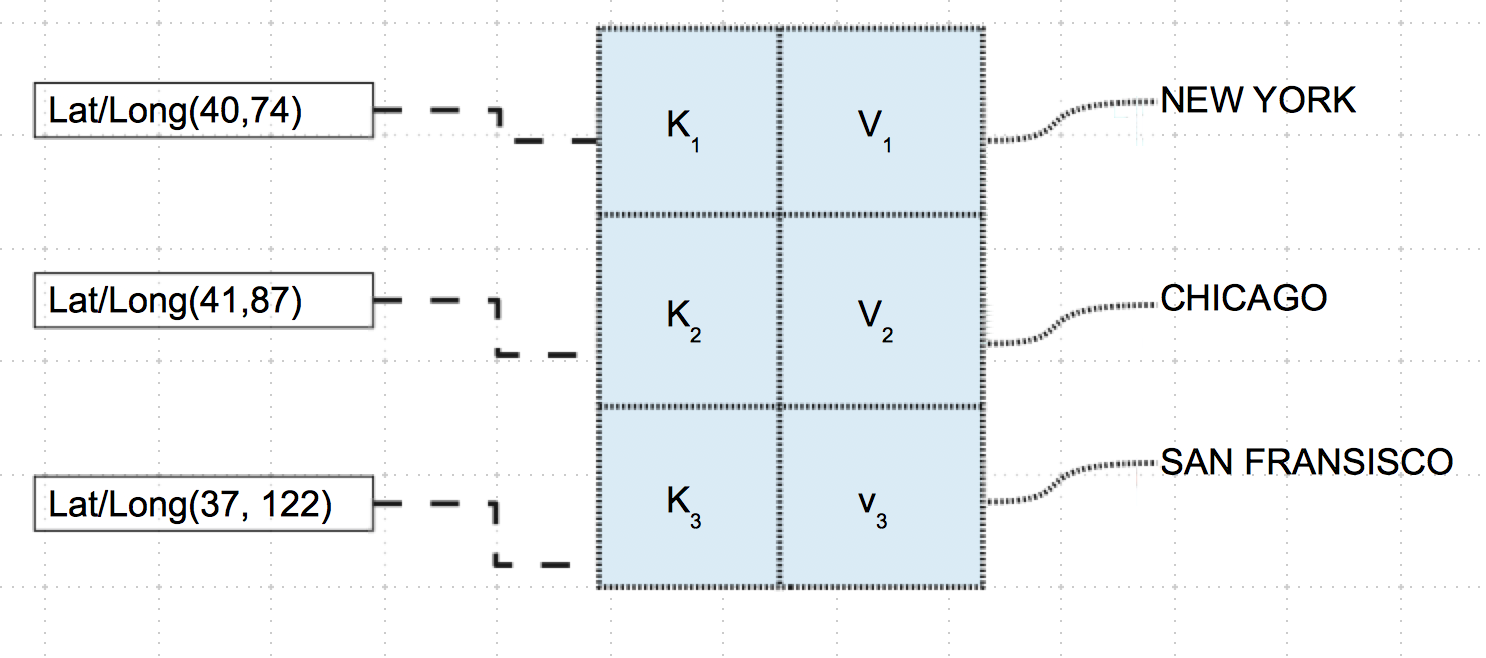
This example Python program shows how a frozenset can be used along with a Python dictionary instance. A set of latitude and longitude values are added as keys of a dictionary instance. The values against the keys are the strings of city names while they could be any complex object. This is possible as the frozenset instances are immutable and hashable.
|
# Example Python program using frozenset as keys of a dictionary # City1 latitude1 = 40 longitude1 = 74
latLong1 = (latitude1, longitude1) cityName1 = "NewYork"
# City2 latitude2 = 41 longitude2 = 87
latLong2 = (latitude2, longitude2) cityName2 = "Chicago"
# City3 latitude3 = 37 longitude3 = 122
latLong3 = (latitude3, longitude3) cityName3 = "San Francisco"
# Create a Python dictionary cityCollection = dict()
# With key as a frozenset instance of latitude and longitude # add cities to the dictionary cityCollection[latLong1] = cityName1 cityCollection[latLong2] = cityName2 cityCollection[latLong3] = cityName3
# Print the dictionary print("Cities by latitude and longitude:") print(cityCollection) |
Output:
|
Cities by latitude and longitude: {(40, 74): 'NewYork', (41, 87): 'Chicago', (37, 122): 'San Francisco'} |