Overview:
- SQLite has two databases, which are always loaded onto it. One is the “main” database and another one is the “temp” database.
- The “temp” database is for storing temporary tables.
- The “main” database and “temp” database can neither be attached nor be detached.
- A database file can be attached to an existing SQLite connection by using the ATTACH statement.
The ATTACH statement in SQLite:
The ATTACH statement in SQLite is of the form,
|
ATTACH DATABASE <database file name> AS <database name> |
- If a database file with the specified file name does not exist a new file will be created.
Example 1- Attach Database:
|
ATTACH DATABASE bill.db AS billing |
The above example will create a database named billing inside the file bill.db and any tables created on the database billing will be saved under the file bill.db.
Example 2- Create a new table in the attached SQLite Database:
Assuming the currency is stored in the lowest denomination such as cents and tax rate is stored as basis points the following statement will create a table with the name cashbill in the SQLite database billing.
|
CREATE TABLE billing.cashbill(id int, itemcode int, rate int, quantity int, price int, taxrate int, tax int, total int) |
The following INSRT statements will populate the newly attached SQLite database billing.cashbill with two records.
|
INSERT INTO billing.cashbill VALUES (1, 256,300,2,600,2,12,612) INSERT INTO billing.cashbill VALUES (2, 272,100,3,300,2,6,306) |
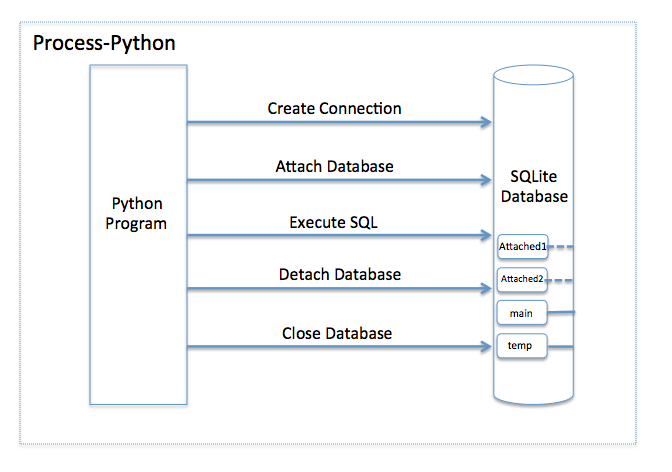
Attaching a SQLite Database using Python:
- The Sqlite3 module acts as the SQLite client using which a Python program can connect to the Sqlite3 database.
- Once Sqlite3 is imported into a python program a connection object can be created to the SQLite main database.
- Through the connection object a cursor object should be obtained using which any SQL statement including the ATTACH DATABASE statement.
- Once the ATTACH DATABASE is executed, the connection object obtained can now be used to access both the main database and the newly attached database.
- The example Python program below attaches a new SQLite database, creates a new table on the attached database and populates two records into the new table.
- The SQLite table is queried and the results are displayed before detaching the database and closing the connection.
Example3- Attaching a SQLite table using Python:
|
# Example Python Program to attach a database file to an existing DB connection
# import the sqlite module import sqlite3
# Create database connection to the sqlite main database connectionObject = sqlite3.connect("primedb.db")
#Obtain a cursor object cursorObject = connectionObject.cursor()
''' Perform operations on the prime db . . . Done with prime db and want to work on billing database using the same database connection '''
# Attach a database file attachDatabaseSQL = "ATTACH DATABASE ? AS billing" dbSpec = ("bill.db",) cursorObject.execute(attachDatabaseSQL,dbSpec)
# Drop any existing tables with the same name cursorObject.execute("drop table billing.cashbill")
# Create billing table in the newly attached database createTableSQL = "CREATE TABLE billing.cashbill(billid int, itemcode int, rate int, quantity int, price int, taxrate int, tax int, total int)" cursorObject.execute(createTableSQL)
# Insert a row of data into the billing.cashbill table billid = 1 itemcode = 256 rate = 300 quantity = 2 price = 600 taxrate = 2 tax = 12 total = 621
insertDataSQL = "INSERT INTO billing.cashbill VALUES (?, ?,?,?,?,?,?,?)"
# Substitution parameters for the insert statement- ? will be replaced by members of this tuple insertSpec = (billid,itemcode,rate,quantity,price,taxrate,tax,total)
#Execute SQL insert using parameter substitution cursorObject.execute(insertDataSQL, insertSpec)
# Commit the changes connectionObject.commit()
# Query the cashbill table querySpec = (billid,)
cursorObject.execute("SELECT * FROM billing.cashbill WHERE billid=?", querySpec)
# print the record print("Fetched record from the attached SQLite database table:"); print(cursorObject.fetchone())
# detach the database detachDatabaseSQL = "DETACH DATABASE billing" cursorObject.execute(detachDatabaseSQL)
# Close the database connection as the resource is no longer needed connectionObject.close() |
Output:
|
Fetched record from the attached SQLite database table: (1, 256, 300, 2, 600, 2, 12, 621) |