Overview:
This is an overview of Python’s socketserver module - a framework for writing network servers/services.
Be it Systems Programming or application programming - Writing network services is a pervasive task in a Programmer's life.
Network Services or Network Servers can be written in two ways:
- Using the Python socket module – which provides the BSD socket interface
- Using the socketserver module which provides specialized framework for writing network servers
Once decided writing a network service is needed - the next set of questions that raise in our minds are
- What kind of a network service it is?
- Should the network service support a protocol that is Connection Oriented, Reliable, and Supports Sessions?
- Or the network service support should support a protocol, which is Discrete, Datagram based, Unreliable but still OK for the task in hand?
- Will the Client connections be processed one by one?
- Will the clients making connections to the network service wait patiently while requests are processed one by one?
- Or is it necessary to handle multiple requests concurrently?
- If Multiple Requests are to be handled concurrently - will separate threads be used for handling each request - or separate processes be used to process each thread?
Based on the decisions made for each of questions above - different type of network servers can be written regardless of the actual applications or semantics they serve.
Python's socketserver module provides the framework through which network servers of all the above kinds and beyond can be written in an extensible way.
Before knowing how each type of network server can be written and which classes from Python's socketserver module to be used - knowing the cookie cutter classes or a set of base classes provides an understanding of how to go about writing any kind of network server.
|
Class Name |
Purpose |
|
BaseServer |
|
|
BaseRequestHandler |
|
Steps involved in creating a network server using Python’s socketserver module:
- Create a request handler by sub classing the BaseRequestHandler and overriding the handle(), setup(), finish() methods
- Create an instance of a BaseServer subclass by passing the network address, port number and the request handler class
- Call the methods handle_request() or serve_forever() on the server instance to process one or more number of requests from the clients.
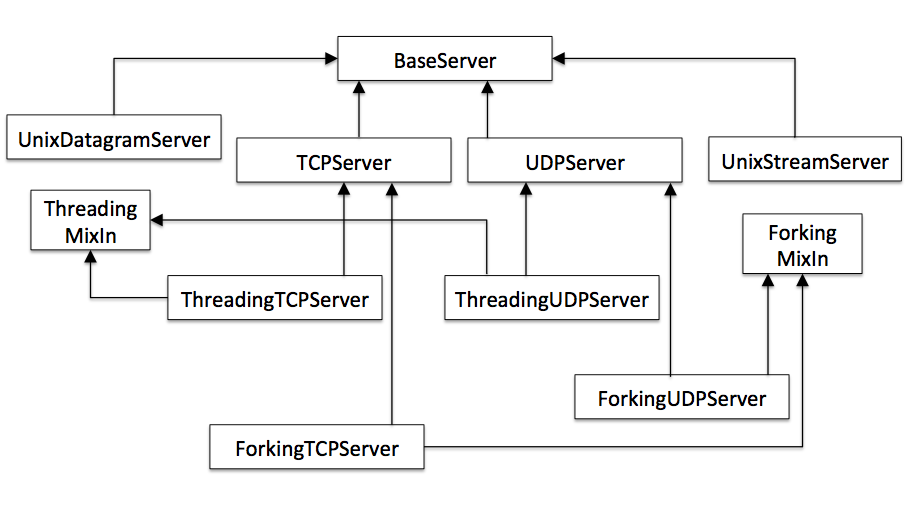
List of Python’s socketserver classes and their purpose:
|
Class Name |
Purpose |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnixStreamServer
|
|
|
UnixDatagramServer
|
|
|
ThreadingMixIn |
|
|
ForkingMixIn |
|
|
ForkingTCPServer |
|
|
ForkingUDPServer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
StreamRequestHandler
|
|
|
DatagramRequestHandler
|
|