Overview:
-
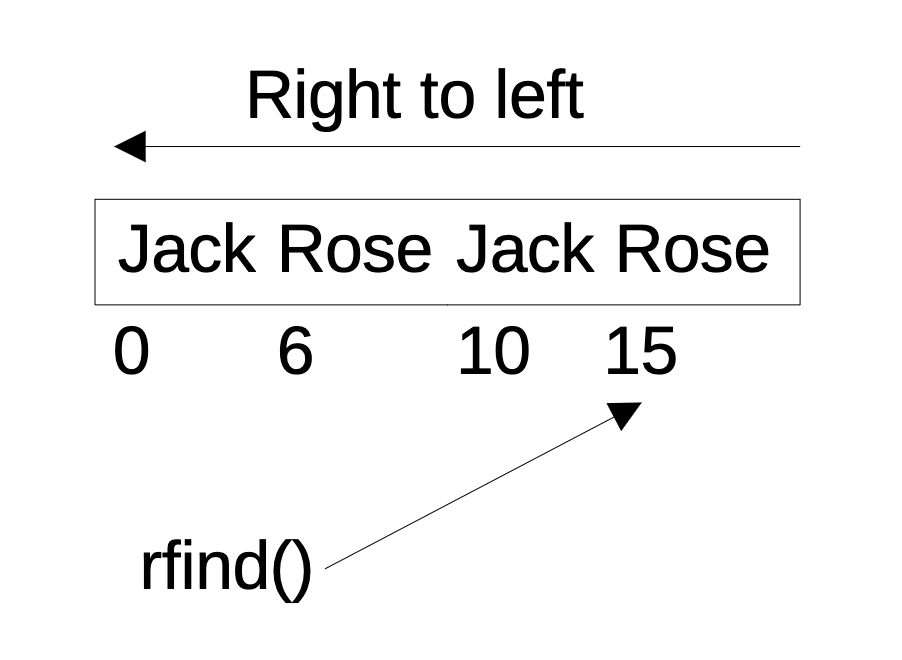
For each string element found in a NumPy array-like the the function numpy.strings.rfind() function finds the highest index at which a substring is available. The indexes are returned as an ndarray of integers.
-
The substring can be searched between a start index and stop index. When start and stop indexes are not specified the string is searched from the position 0 to length – 1.
-
If the input parameter is a scalar, the rfind() function returns an integer denoting the highest index position at which a substring is found in the string.
-
The function works for unicode strings (numpy.str_), byte strings(numpy.bytes_) and variable width strings(numpy.dtypes.StrDType).
-
When a NumPy array is created with elements having type as Python string NumPy converts it into a NumPy array of numpy.str_ type.
Example:
|
# Example Python program that finds # Create an ndarray containing texts of variable length lines[0][0] = "Rose is a rose is a rose is a rose." # Find the substring |
Output:
|
Text lines: [['Rose is a rose is a rose is a rose.' 'Jack Rose Jack Rose.' 'It is rose in hen.']] Substr "Rose" found in indexes: [[ 0 15 -1]] |