Overview:
- The fromhex() method converts hexadecimal digits from a string, bytes or from a bytes-like object into a bytearray.
- The method accepts even number of hexadecimal digits and returns a bytearray object. The input cannot be odd number of digits as the resultant bytearray can have only “n” number of bytes. It cannot have fractions of a byte, like a half byte. When odd number of digits are passed as the input, the method fromhex() will raise an exception stating “ValueError: fromhex() arg must contain an even number of hexadecimal digits”.
- The input parameter cannot contain any non-hexadecimal number. For example, the string “ABC%” cannot be converted using fromhex() as the input string has non-hexadecimal digits.
Note:
1 bit represents up to 2 values – 0 and 1.
2 bits represent up to 4 values – 00, 01, 10, 11.
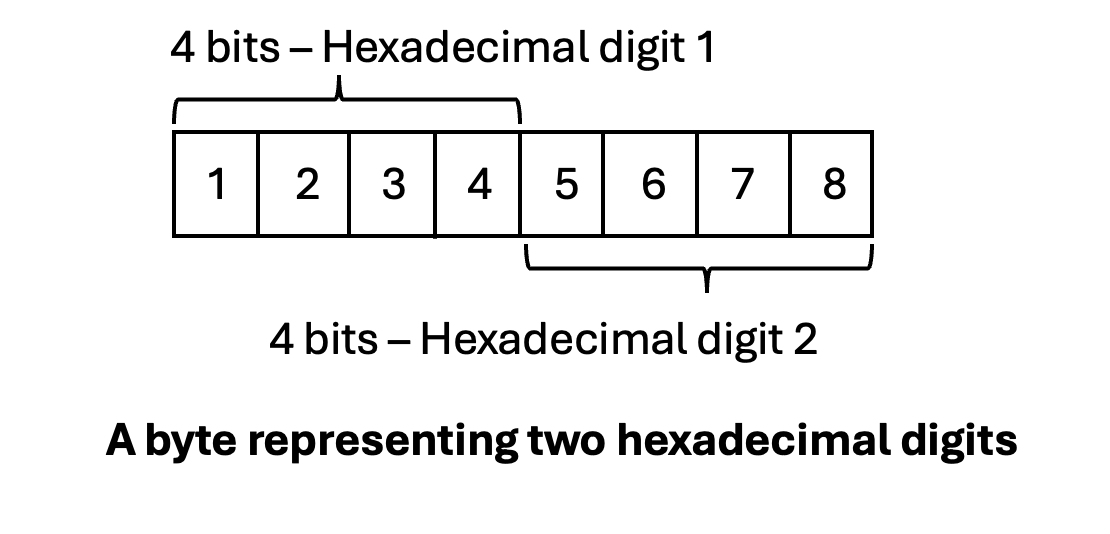
4 bits represent up to 16 values - 0000, 0001, 0010, 0011, 0100, 0101, 0110, 0111, 1000, 1001, 1010, 1011, 1100, 1101, 1110, 1111. One hexadecimal digit can be represented using 4 bits. A byte can represent two hexadecimal digits.
Example 1 - Create a bytearray from a string of hexadecimal digits:
|
# Example Python program that converts the # Convert to bytearray print("The bytearray:") print("Length of the bytearray:") |
Output:
|
The bytearray: |
Example 2 - Create a bytearray from a bytes-like object:
|
# Example Python program that converts the # Convert to bytearray print("The bytearray object:") |
Output:
| The bytearray object: bytearray(b'\x01\x02\x0e\x0f') |