Overview:
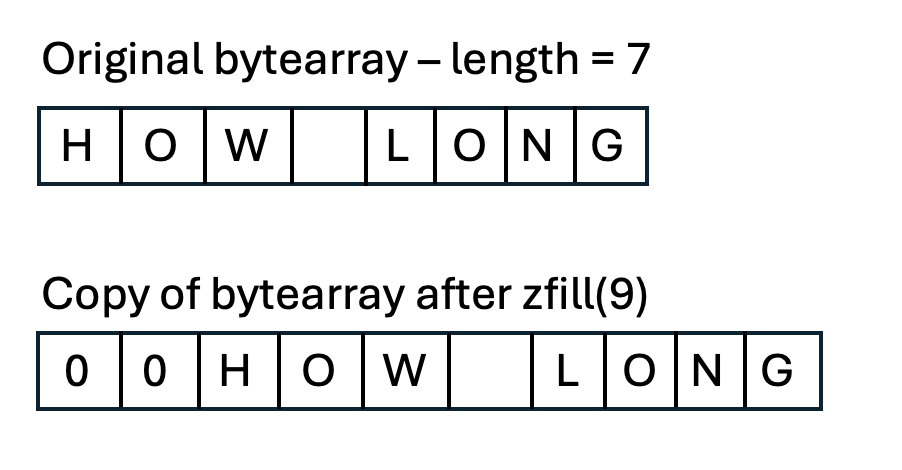
The zfill() method returns a new bytearray object of a given size which is zero-filled on the left side. The zfill() returns a zero padded bytearray on the left side, only when the given size is greater than the current size of the bytearray. If the given size is less than the current size, a copy of the original bytearray is returned without any modification.
Though the resize() and zfill() methods are about changing the size of a bytearray the following are the differences between them:
| The zfill() method | The resize() method | |
| When buffer less than current size | When a size less than the current size is specified the zfill() method returns the copy of the original bytearray. | The reset method will reduce the size of the original bytearray when a size less than the current size is specified. |
| Zero fill location | The zfill() method zero-fills on the left side of the bytearray and returns the new bytearray. The original bytearray is not modified. | When the size given is greater than current size it zero-fills the left side of the original bytearray. |
| Copy vs actual bytearray | Changes are made to the copy of the bytearray. | Changes are made to the original bytearray. |
Example:
|
# Example Python program that creates a new # Create a bytearray # Create a new bytearray which is zfilled print("Original bytearray:") print("The zfilled bytearray:") |
Output:
| Original bytearray: bytearray(b'The lazy brown fox') Id:4340038960 The zfilled bytearray: bytearray(b'0000The lazy brown fox') Id:4340038896 |