Overview:
- The deque is a container class in Python which can hold a collection of Python objects.
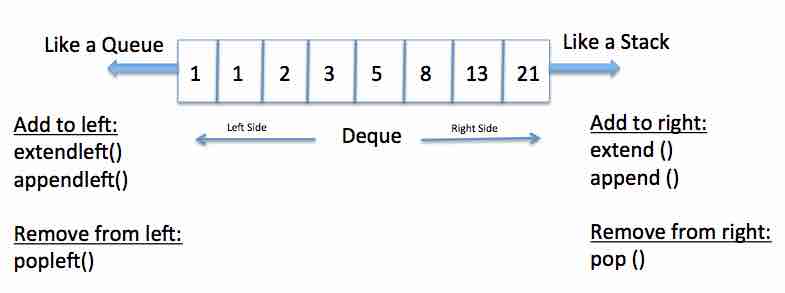
- A deque is a double-ended queue on which elements can be added or removed from either side - that is on left end or right end, head or tail.
- A deque is like both a stack and queue.
- On a deque, adding an element or removing an element on either side of a deque instance takes constant time O(1).
Example:
|
import collections
# create an empty deque d1 = collections.deque()
# add few elements to the right side of the deque d1.append(10) d1.append(10.1) d1.append("abc")
print("Contents of the deque") print(d1) |
Output:
|
Contents of the deque deque([10, 10.1, 'abc']) |
Example2 - Creation of a deque from an iterable object:
|
import collections
# A tuple of prime numbers primeNumbers = (3,5,7)
#create a deque from an already existing iterable object - in this case a tuple primeDeque = collections.deque(primeNumbers) print("Initial deque:") print(primeDeque) primeDeque.append(11) primeDeque.append(13) primeDeque.append(13) primeDeque.appendleft(2) print("Deck after append and appendleft:") print(primeDeque) |
Output:
|
Initial deque: deque([3, 5, 7]) Deck after append and appendleft: deque([2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 13]) |
A python deque instance can be initialized using a python iterable object as well.
Elements can be added to and removed from the deque subsequently from either side of the deque.
Example 3 - Creation of a deque from an iterable object:
|
import collections
# create a fixed size deque dequeInstance = collections.deque(maxlen=5)
# add 5 elements to the right side dequeInstance.append(10) dequeInstance.append(20) dequeInstance.append(30) dequeInstance.append(40) dequeInstance.append(50)
print(dequeInstance)
# add 1 element to the right side dequeInstance.append(60) print(dequeInstance)
# add 1 element to the left side dequeInstance.appendleft(5) print(dequeInstance) |
Output:
|
deque([10, 20, 30, 40, 50], maxlen=5) deque([20, 30, 40, 50, 60], maxlen=5) deque([5, 20, 30, 40, 50], maxlen=5) |
When the deque is specified of a maximum length using maxlen parameter and the deque has reached the maximum length, if an element is added to the left side one element is removed from the right side; when an element is added to the right side one element is removed from the left side.
Deque methods:
|
|
The append() method adds one element to the right side of a deque instance, as specified the elem parameter. |
|
|
The appendleft() method adds an element to the left side of a deque instance. |
|
|
The clear() removes all the elements from a python deque instance. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| extend() | Adds more elements to a Python deque instance from a Python iterable. |
| extendleft() | While the extend() method of deque makes it grow on the right side, the extendleft() makes the deque to grow on the left side. Both extend() and extendleft() uses another Python iterable to grow. |
| index() |
The index method searches for a given element between the start and stop positions. When no start and stop positions are specified the whole deque is searched. The position at which the element is found is returned. If no element is found an exception of type ValueError is raised. |
| insert() |
Inserts an element at the specified position in a deque. |
| Removes an element from the right side of a deque and returns it. | |
| popleft() | Removes an element from the left side of a deque and returns it. |
| remove() | Removes the first occurence of an element and returns it. |
| reverse() |
The reverse() method reverses the arrangement of elements in a deque. |
| rotate() |
The rotate() method rotates the arrangement of elements in a deque by specified number of times. |