Overview of TLS1.3 and Python support for TLS/SSL
History of TLS:
Two endpoints in a computer network can communicate in a secure way using the TLS protocol (Transport Layer Security). Providing secure communication for mainstream usage was introduced through SSL (Secure Socket Layer) in 1995 by Netscape Corporation. TLS 1.0 was introduced in 1999 and has undergone major revisions leading to the next version TLS 1.2 in 2008. The current version of the protocol is TLS 1.3 as of August 2018.
How TLS works:
TLS uses a combination of the following cryptographic methodologies and infrastructure to provide secure data communication between a server and a client,
- Symmetric key cryptography
- Asymmetric Key cryptography
- Public key infrastructure
- Key exchange mechanisms
- Message digests
Encrypting TLS sessions with symmetric key cryptography:
To deliver a message over the network in a secure way – the message must be encrypted with the strongest cryptographic algorithm. TLS mandates that one of the following combination of algorithms to be used between network two endpoints.
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_128_CCM_8_SHA256
These combinations are called cipher suits.The cryptographic algorithms used in TLS: AES_128, AES_256 and CHACHA20 are all symmetric in nature meaning the same key that is used during the encryption process is used for decryption as well.
TLS and AEAD:
All the five cipher suits permitted in TLS1.3 provides Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data(AEAD). Mere encryption of the data provides confidentiality. However, the user receiving the encrypted data is not guaranteed with the authenticity of the data. When an algorithm like AES is combined with GCM mode it takes the plain text, a key and associated data. Using the encrypted text and the associated data(not encrypted) the algorithm computes a tag and sends it along with the cipher text and associated data. The user receiving the cipher text can compute the tag using the same algorithm and ensure that the cipher text and associated data are not tampered in transit. Thus, an AEAD algorithm guarantees both confidentiality and authenticity of the cipher text and the associated data.The AES algorithm from the cipher suit TLS_AES_128_GCM applies AES in Galois/Counter Mode.
Ephemeral session keys:
The symmetric encryption key used for the communication is valid only for a single TLS session. For the next TLS session a new encryption key is used. Thus, the session keys used in TLS are ephemeral keys which are discarded at the end of the session(i.e., Upon the close_notify alert and other corner cases). Having ephemeral keys for communication incorporates Perfect Forward Secrecy into the communication.
In TLS no session key is transmitted over the network in any form as it uses the Diffie–Hellman key exchange method for generating the same session key from both client and server sides. Even on the extreme event of an attacker knowing a session key, will not make the whole communication compromised. The previous and subsequent data transfers will be secure as the session keys are ephemeral in nature which is valid only for one session.
Generating symmetric session keys:
TLS mandates the key exchange mechanism for generating the ephemeral session keys to any of following:
• DHE - Diffie-Hellman key Exchange
• ECDHE - Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral
How Diffie-Hellman key exchange works in TLS:
The server generates a big prime number(p) and a primitive root(g) and stores it in its cache. Both p and g are shared with the client in plain text format. Both client and server also generate random numbers a and b which they keep as a secret. Using p, g and a client calculates a value A, using the formula A = ga mod p. Using p, g and b the server calculates a value, B = gb mod P.
The client calculates the shared key S = Ba mod p.
The server calculates the shared key S = Ab mod p.
Now both client and server have the key S – which is called a shared key, which will be used in encrypting and decrypting the data using one of the symmetric key algorithms AES_128, AES_256 and CHACHA20.
The sharing of a symmetric key used for encrypting the data happens without the keys ever travelling through the computer network. What travel over the network is the public values p and g and the key shares A and B. A is the client key share using which the server computes the symmetric key also known as the session key. B is the server key share using which the client computes the session key.
This computing of key shares and actual key happen many times - once per a TLS session and thus providing perfect forward secrecy.
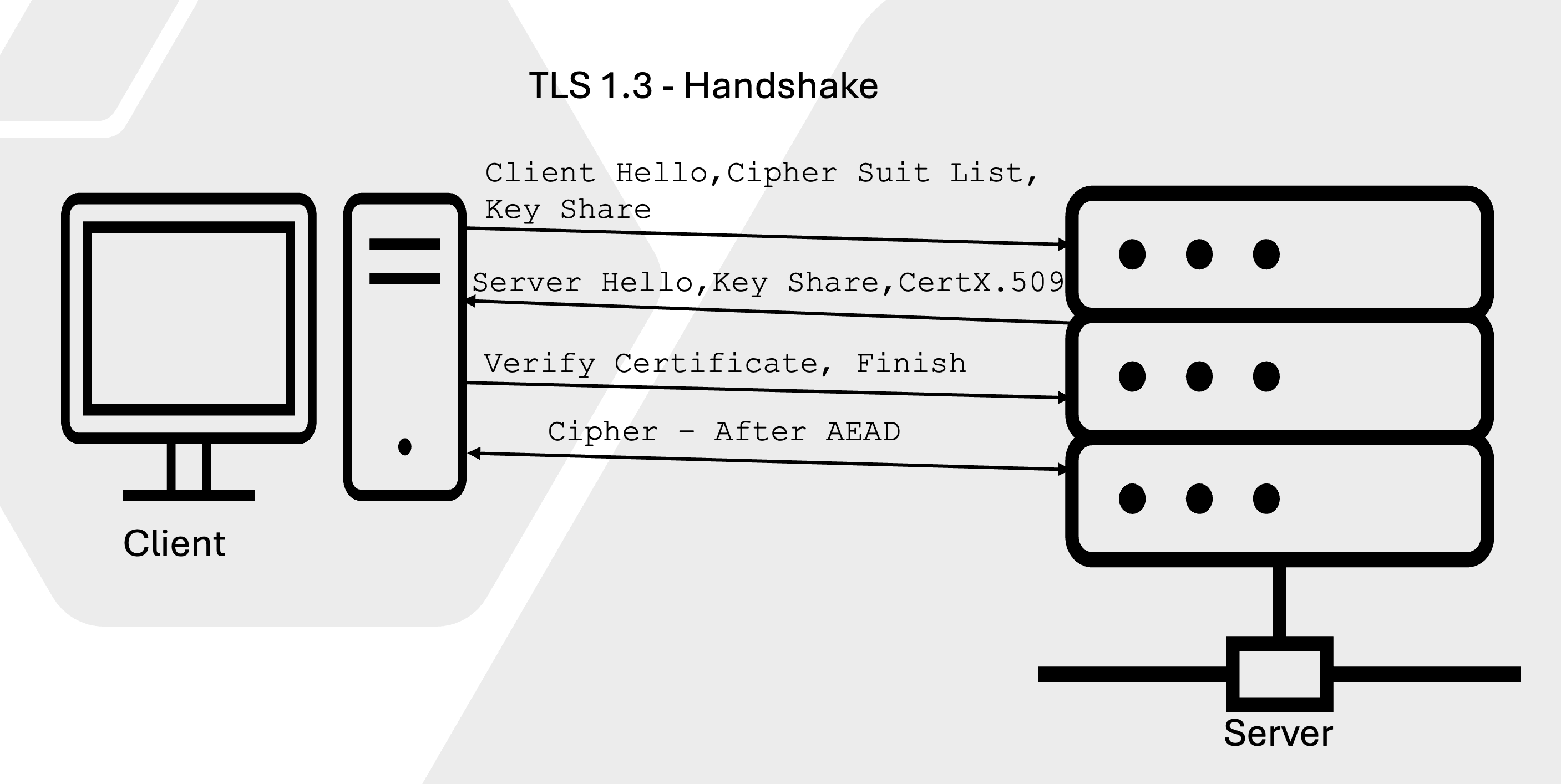
In short, the client sent a list of cipher suits to which the server responded with public values p and g, the selected cipher suit, the X.509 certificate of the server. Key exchange happens through sharing of key shares and subsequent calculation of the session key. This is called the TLS1.3 handshake which establishes a TLS session.
Verifying the digital certificate of the server:
As part of the “server hello” message from the server a digital certificate of the server in X.509 format is sent to the client. The digital certificate bears the signature of the server and the signature-algorithm. The client authenticates the identity of the server by de-signing the digital signature using its public key and comparing with the message digest calculated at the client side. If both are equal, then the client asserts that the certificate and the signature is from the actual server.
TLS1.3 handshake:
In this article as we had an inside out view – we started with the encryption of the data using the symmetric cypher. This requires a pre-establishment of ephemeral session keys using Diffie-Helman key Exchange. We also talked about how the X.509 certificate is validated at the client side. Now, it is time to order things chronologically and draw the TLS1.3 handshake.
Python standard library and TLS/SSL:
- The ssl module of Python standard library provides classes that help implementing secure communication between two network endpoints using TLS protocol.
- The name of the module ssl is purely historic and the module supports the current version of the TLS that is version 1.3, older versions of the TLS and the SSL.
- The popular open-source library OpenSSL implements both SSL and TLS specifications and the library is written in the C
programming language. - The Python module ssl uses OpenSSL as the underlying library to provide TLS/SSLs upport in Python.
- The Python ssl module provides the classes SSLSocket and SSLContext to implement secure communication using TLS.
- The SSLSocket class is derived from the socket class. The socket class provides implementation of a streaming socket (TCP Socket) and the SSLSocket provides SSL handshake and encryption functionalities. Hence the SSLSocket is derived from the socket class the SSLSocket provides streaming communication as well as cryptographic services.
- The SSLContext has support for reading - X.509 certificates of the root certificate authorities, intermediate certificate authorities and the servers.