Overview:
Python supports logical operator AND through the "and" keyword. In mathematics, the "AND" operation returns true only if both the operands evaluate to True. Otherwise the AND operation returns False. In Python the "and" operator returns the first operand if the first operand evaluates to False. Otherwise, it returns the second operand.
The "and" operator in Python is a short circuit operator. The second operator will be evaluated by the "and" operator only if the first operand evaluated to True.
Truth Table for the 'and' operator:
|
Operator 1 |
Operator 2 |
Result of AND |
|
True |
True |
True |
|
True |
False |
False |
|
False |
True |
False |
|
False |
False |
False |
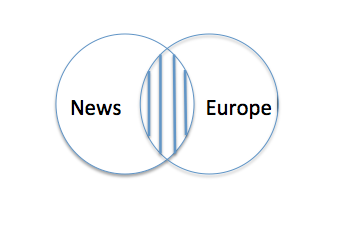
Ven Diagram for the 'and' operator :
The Ven diagram of the and operator is given below. This Ven diagram is about a search criteria, stating the search results should include News that is only about Europe.
Example 1:
|
signal = "Green" path = "Pedestrian walking"
if signal is "Green" and path is "clear": print("All clear and Going") else: print("Can not go") print("Reason:%s"%(path)) |
Output:
|
Can not go Reason:Pedestrian walking |
Example 2:
|
filter1 = True filter2 = True
if filter1 is True and filter2 is True: print("Printing Search Results") else: print("Search could not find any results") |
Output:
|
Printing Search Results |