Overview:
- The numpy.ndarray supports cumulative sum and cumulative product of the n dimensional arrays.
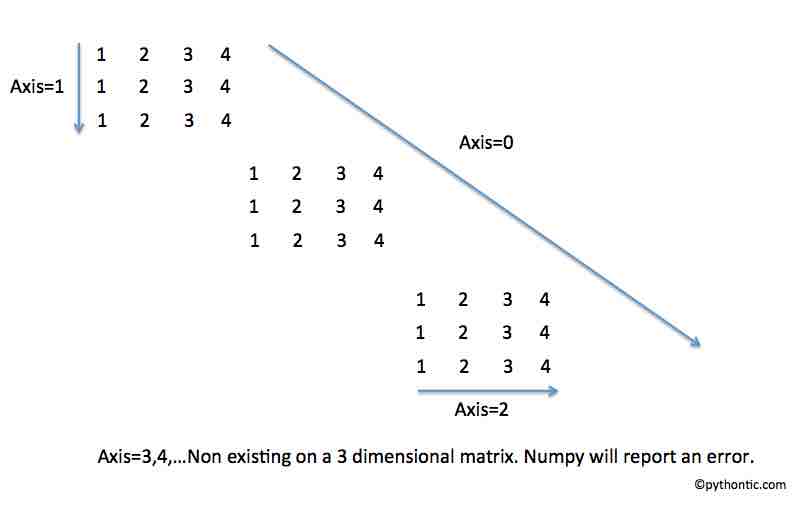
- When cumulative sum or cumulative product is performed for a 1 dimensional array, the number of axes is 1. For a 2 dimensional array number of axis is 2 and for a 3 dimensional array number of axes is 3 and so on.
- When cumulative sum or cumulative product is performed for a one-dimensional array the axis parameter of cumsum() or cumprod() will take a value of 0. For a two dimensional array the axis parameter of cumsum() or cumprod() will take the values 0, 1 and for a three dimensional array the axis parameter of cumsum() or cumprod() will take the values 0, 1, 2 and so on.
- The diagram below illustrates how the cumsum() or cumprod() work in numpy on an ndarray object.
Example - numpy.ndaray.csum:
|
# Example Python program demonstrating cumulative sum of a numpy.ndarray
# Import numpy module import numpy as np
# Import standard library module random import random
# Create a 3 dimensional ndarray object array_3d = np.array([[[1,2,3,4], [1,2,3,4], [1,2,3,4]],
[[1,2,3,4], [1,2,3,4], [1,2,3,4]],
[[1,2,3,4], [1,2,3,4], [1,2,3,4]]]) print("Maximum value allowed for axis object for a 3 dimensional array:%d"%(array_3d.ndim-1)) print("Shape of the array: %d,%d,%d"%(array_3d.shape[0],array_3d.shape[1],array_3d.shape[2]))
print("Original Array:") print(array_3d)
print("Cumulative Sum along Axis 0:") csum = array_3d.cumsum(axis=0) print(csum)
print("Cumulative Sum along Axis 1:") csum = array_3d.cumsum(axis=1) print(csum)
print("Cumulative Sum along Axis 2:") csum = array_3d.cumsum(axis=2) print(csum)
|
Output:
|
Maximum value allowed for axis object for a 3 dimensional array:2 Shape of the array: 3,3,4 Original Array: [[[1 2 3 4] [1 2 3 4] [1 2 3 4]]
[[1 2 3 4] [1 2 3 4] [1 2 3 4]]
[[1 2 3 4] [1 2 3 4] [1 2 3 4]]] Cumulative Sum along Axis 0: [[[ 1 2 3 4] [ 1 2 3 4] [ 1 2 3 4]]
[[ 2 4 6 8] [ 2 4 6 8] [ 2 4 6 8]]
[[ 3 6 9 12] [ 3 6 9 12] [ 3 6 9 12]]] Cumulative Sum along Axis 1: [[[ 1 2 3 4] [ 2 4 6 8] [ 3 6 9 12]]
[[ 1 2 3 4] [ 2 4 6 8] [ 3 6 9 12]]
[[ 1 2 3 4] [ 2 4 6 8] [ 3 6 9 12]]] Cumulative Sum along Axis 2: [[[ 1 3 6 10] [ 1 3 6 10] [ 1 3 6 10]]
[[ 1 3 6 10] [ 1 3 6 10] [ 1 3 6 10]]
[[ 1 3 6 10] [ 1 3 6 10] [ 1 3 6 10]]] |
Example - numpy.ndaray.cumprod:
|
# Example Python program demonstrating cumulative product of a numpy.ndarray
# Import numpy module import numpy as np
# Import standard library module random import random
# Create a 2-dimensional ndarray object array_2d = np.array([[1,1,1,1], [2,2,2,2], [3,3,3,4]])
print("Maximum value allowed for axis object for a 2 dimensional array:%d"%(array_2d.ndim-1)) print("Shape of the array: %d,%d"%(array_2d.shape[0], array_2d.shape[1]))
print("Original Array:") print(array_2d)
print("Cumulative Product along Axis 0:") cproduct = array_2d.cumprod(axis=0) print(cproduct)
print("Cumulative Product along Axis 1:") cproduct = array_2d.cumprod(axis=1) print(cproduct) |
Output:
|
Maximum value allowed for axis object for a 2 dimensional array:1 Shape of the array: 3,4 Original Array: [[1 1 1 1] [2 2 2 2] [3 3 3 4]] Cumulative Product along Axis 0: [[1 1 1 1] [2 2 2 2] [6 6 6 8]] Cumulative Product along Axis 1: [[ 1 1 1 1] [ 2 4 8 16] [ 3 9 27 108]] |