Overview:
- Data with size ranging from few lines to millions of lines are generated daily as CSV streams and files or delimiter separated streams and files. Examples of such data sources include Stock Exchanges, Weather Stations, Sensors in factory Settings, Computer Programs monitoring for various events and so on.
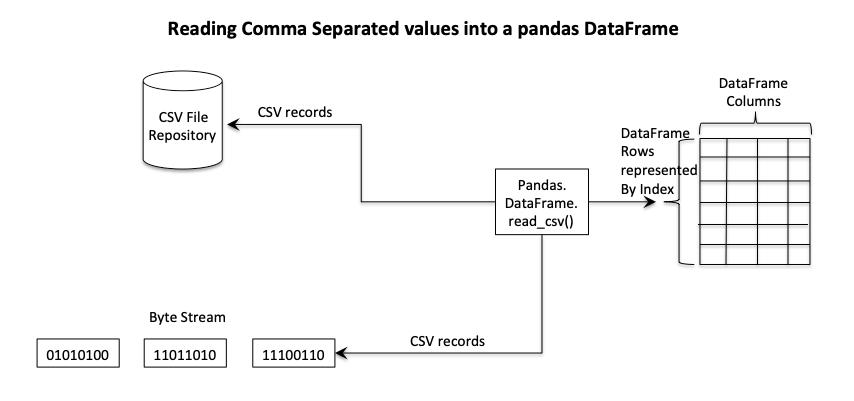
- In a comma-separated file, commas separate fields and every record starts in a new line.
- The pandas DataFrame class supports serializing and de-serializing of CSV in an extenstive way through the read_csv() method.
- The read_csv() method of pandas DataFrame class reads a CSV file and loads each record as a row in the DataFrame.
- In the similar way the pandas DataFrame class supports operations like reading and writing DataFrame contents from/to MySQL; and reading and writing DataFrame contents from/to PostgreSQL.
Example–To load data from a CSV file into a pandas DataFrame:
|
# Example Python program to read a CSV file # and load the contents into a pandas DataFrame object import pandas as pds
# Name of the CSV file fileName = "./ServerResponseTimes.csv";
# Read CSV file into a pandas DataFrame instance dataFrame = pds.read_csv(fileName);
# Print the contents of the DataFrame onto the console print("Contents of the DataFrame as read from the .csv file:"); print(dataFrame);
# Print the index of the DataFrame print("Index of the DataFrame:"); print(dataFrame.index); |
Output:
|
Contents of the DataFrame as read from the .csv file: Server Name Response Time(ms) 0 Host1 12 1 Host2 25 2 Host3 10 3 Host4 40 4 Host5 71 Index of the DataFrame: RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1) |
Example-To load a binary stream of CSV records into a pandas DataFrame:
The read_csv() is capable of reading from a binary stream as well. The Python example code below constructs a bytes literal and creates a BytesIO stream out of it. The byte stream is passed to the read_csv() method which parses the bytes from the stream and loads into a DataFrame.
|
# Example Python program to load data from a binary stream of CSV # into a pandas DataFrame import pandas as pds import io
# Create a CSV bytes literal csvData = b"Symbol, Price \r\n Example1, 10 \r\n Example2, 20";
# Make a binary stream binaryStream = io.BytesIO(csvData);
# Make pandas to read the CSV from the binary stream and load it into a DataFrame dataFrame = pds.read_csv(binaryStream); print("Contents of the DataFrame loaded from a binary stream of CSV:") print(dataFrame); |
Output:
|
Contents of the DataFrame loaded from a binary stream of CSV: Symbol Price 0 Example1 10 1 Example2 20 |