Overview:
- Pandas DataFrame class supports storing data in two-dimensional format using nump.ndarray as the underlying data-structure.
- The DataFrame contents can be written to a disk file, to a text buffer through the method DataFrame.to_csv(), by passing the name of the CSV file or the text stream instance as a parameter.
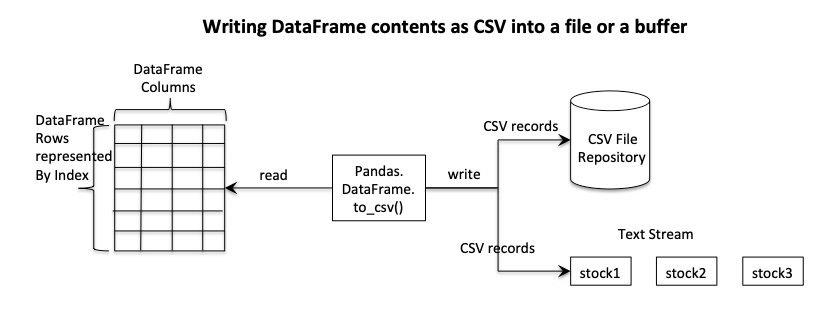
Example - To write the contents of a pandas DataFrame as a CSV file:
The Python example below writes the contents of a DataFrame which has volume data of three stocks for five trading days into a CSV file in the current working directory.
|
# Example Python program to write the contents of a # DataFrame into a CSV file import pandas as pds
# Name of the CSV file csvFileName = "./Volumes.csv"
# Create a dictionary of lists for stock vs volume data volumes = {"Stock1":[53871, 48421, 51761, 57987, 58900], "Stock2":[45012, 44521, 45569, 44732, 44721], "Stock3":[67540, 62890, 66743, 68900, 71456]};
# Load data into a DataFrame instance dataFrame = pds.DataFrame(data=volumes); dataFrame.index = ("Day 1", "Day 2", "Day 3", "Day 4", "Day 5");
# Write contents of the DataFrame to a CSV file dataFrame.to_csv(csvFileName); |
Output:
Contents of the CSV file Volumes.csv as written by the above example is given here.
|
,Stock1,Stock2,Stock3 Day 1,53871,45012,67540 Day 2,48421,44521,62890 Day 3,51761,45569,66743 Day 4,57987,44732,68900 Day 5,58900,44721,71456 |
Example - To get the contents of a pandas DataFrame as a CSV String:
This Python example program creates a DataFrame from a Python dictionary and gets the DataFrame contents as a CSV string by calling DataFrame.to_csv() method, without passing any parameters.
|
# Example Python program to get the contents of a DataFrame as a CSV string import pandas as pds
# Standard deviations in the thickness of three wooden board variants in mm standardDeviations = {"Wood 1": [0.4, 0.5, 0.3], "Wood 2": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3], "Wood 3": [0.7, 0.6, 0.7] };
# Load data into a DataFrame instance dataFrame = pds.DataFrame(data=standardDeviations, index=("Variant1", "Variant2", "Variant3"));
# Get the contents of the DataFrame as a CSV file csv=dataFrame.to_csv(); print("Contents of the DataFrame as a CSV string:") print(csv); |
Output:
|
Contents of the DataFrame as a CSV string: ,Wood 1,Wood 2,Wood 3 Variant1,0.4,0.1,0.7 Variant2,0.5,0.2,0.6 Variant3,0.3,0.3,0.7 |
Example - To write a pandas DataFrame into a text buffer:
This Python example passes an instance of a text stream like StringIO() to write the DataFrame as a CSV into the in-memory text buffer.
|
# Example Python program to write the contents of a DataFrame to a buffer import pandas as pds from io import StringIO
# Closing price of 3 different stocks over 5 trading days closingPrices = {"Stock1": [34.17, 34.25, 34.2, 34.24, 34.3], "Stock2": [10.01, 10.20, 10.1, 10.15, 10.2], "Stock3": [41.6, 42.1, 41.89, 42.4, 42.7] };
# Load data from the Python dictionary into a DataFrame instance dataFrame = pds.DataFrame(data=closingPrices);
# Create an in-memory text stream textStream = StringIO();
# Write the DataFrame contents to the text stream's buffer as a CSV dataFrame.to_csv(textStream);
print("DataFrame as CSV (from the buffer):");
# Print the buffer contents print(textStream.getvalue()); |
Output:
|
DataFrame as CSV (from the buffer): ,Stock1,Stock2,Stock3 0,34.17,10.01,41.6 1,34.25,10.2,42.1 2,34.2,10.1,41.89 3,34.24,10.15,42.4 4,34.3,10.2,42.7 |