Overview:
Computing world predominantly handles data in two formats:
- Big Endian Format
- Little Endian Format
While most machines handle data in Little Endian Format the network transmission and the Internet is using Big Endian Format. Hence, before sending data to the network and after receiving data from the network, the translation to Network Order ie, to Big Endian Order and vice versa is a routine task.
Note that, Java runtimes use Big Endian Format. Python’s Endianness is same as the processor in which the Python interpreter is run.
The socket module of Python provides functions to handle translations of integers of different sizes from Little Endian to Big Endian and vice versa.
Little Endian and Big Endian Explained:
A 32-bit integer has four bytes, each byte comprising of 8 bits.
In Little Endian Format, least significant byte(LSB) will be placed in the lowest address and the most significant byte(MSB) will be placed in the highest address.
For example, if the starting address is X, the least significant byte will be placed in X, and the next least significant byte will be placed in X+1, the next least significant byte at X+2 and the most significant byte will be placed in X+3. In Little Endian, the LSB is stored at the smallest address.
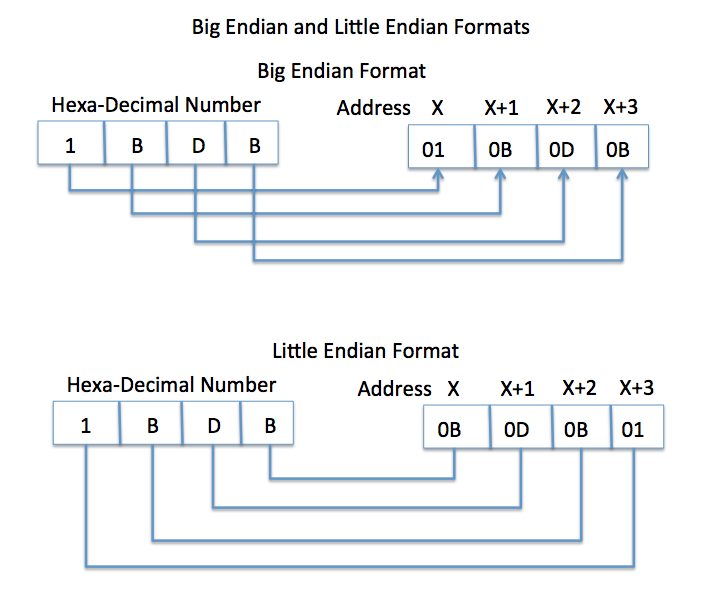
In Big Endian format, most significant byte will be placed in the lowest address and the least significant byte will be placed in the highest address.
For example, if the starting address is X, the most significant byte will be placed in X, and the next most significant byte will be placed in X+1, the next most significant byte at X+2 and the least significant byte will be placed in X+3. The MSB is stored at the smallest address.
The name "Endian" comes from Jonathan Swift's novel "Gulliver's Travels", where some people prefer to eat their hard-boiled eggs from the little end while others eat them from the big end.
How Network Communications work:
In computer networks, while transmitting and receiving data packets, they are sent using Big Endian Order. The reason is, the network protocol suits present in any operating system sends their data frames and fields in this format as defined by the RFC 1700.
RFC 1700, titled ASSIGNED NUMBERS states "express numbers in decimal and to picture data in "big-endian" order".
However, several operating systems and machines deal data in Little Endian Format. So, when a host is following Little Indian Format, the data received over the network needs to be translated into Little Indian Format or the Host Format.
Byte Ordering Functions:
The socket module of Python provides functions for translating host order to network order and vice versa.
|
Python Function Name |
Description |
Translation Direction |
|
socket.ntohl(Int32bit_postive) |
|
Big Endian to Little Endian |
|
socket.ntohs(Int32bit_postive) |
|
Big Endian to Little Endian |
|
socket.htonl(Int32bit_postive) |
|
Little Endian to Big Endian |
|
socket.htons(Int16bit_postive) |
|
Little Endian to Big Endian |
Example:
|
import socket
Int32Bit = 214748300 Int16Bit = 400
#Convert a 32 bit integer from network byte order to host byte order Int32InHostFormat = socket.ntohl(Int32Bit)
#Convert a 16 bit integer from network byte order to host byte order Int16InHostFormat = socket.ntohs(Int16Bit)
print("32 bit integer {} converted from Network Byte Order to Host Byte Order: {}".format(Int32Bit, Int32InHostFormat)) print("16 bit integer {} converted from Network Byte Order to Host Byte Order: {}".format(Int16Bit, Int16InHostFormat))
# Convert a 32 bit integer from host byte order to network byte order Int32InNetworkFormat = socket.htonl(Int32InHostFormat)
# Convert a 16 bit integer from network byte order to host byte order Int16InNetworkFormat = socket.htons(Int16InHostFormat)
print("32 bit integer {} converted from Host Byte Order to Network Byte Order: {}".format(Int32InHostFormat, Int32InNetworkFormat)) print("16 bit integer {} converted from Host Byte Order to Network Byte Order: {}".format(Int16InHostFormat, Int16InNetworkFormat))
|
Output:
|
32 bit integer 214748300 converted from Network Byte Order to Host Byte Order: 2362231820 16 bit integer 400 converted from Network Byte Order to Host Byte Order: 36865 32 bit integer 2362231820 converted from Host Byte Order to Network Byte Order: 214748300 16 bit integer 36865 converted from Host Byte Order to Network Byte Order: 400 |