UDP Overview:
UDP is the abbreviation of User Datagram Protocol. UDP makes use of Internet Protocol of the TCP/IP suit. In communications using UDP, a client program sends a message packet to a destination server wherein the destination server also runs on UDP.
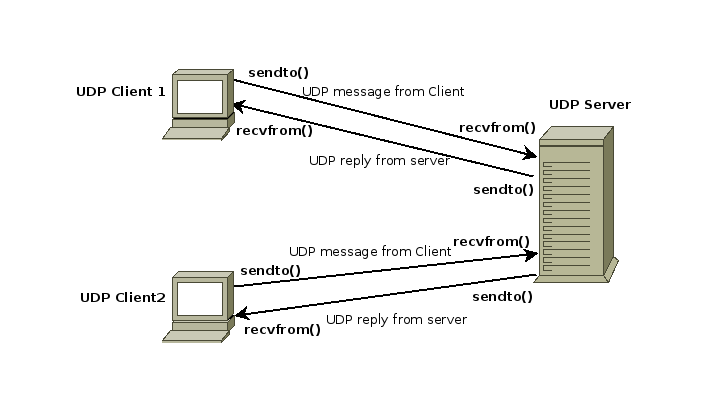
Properties of UDP:
- The UDP does not provide guaranteed delivery of message packets. If for some issue in a network if a packet is lost it could be lost forever.
- Since there is no guarantee of assured delivery of messages, UDP is considered an unreliable protocol.
- The underlying mechanisms that implement UDP involve no connection-based communication. There is no streaming of data between a UDP server or and an UDP client.
- An UDP client can send "n" number of distinct packets to an UDP server and it could also receive "n" number of distinct packets as replies from the UDP server.
- Since UDP is connectionless protocol the overhead involved in UDP is less compared to a connection based protocol like TCP.
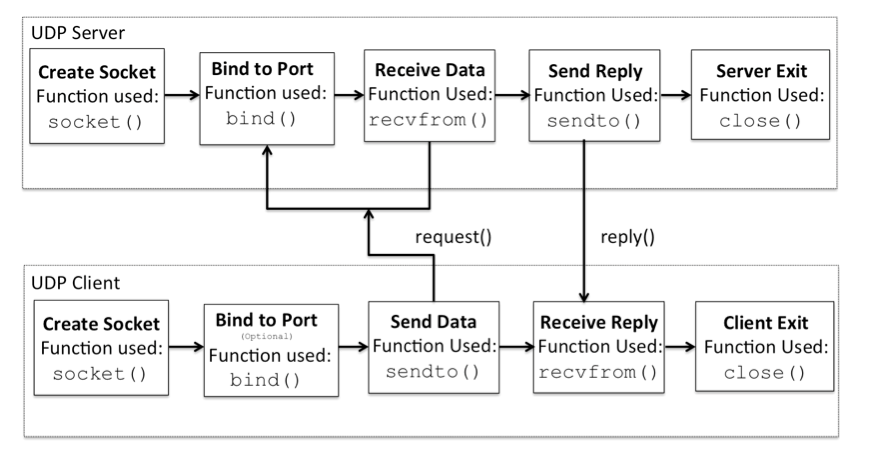
Example: UDP Server using Python
|
import socket
localIP = "127.0.0.1" localPort = 20001 bufferSize = 1024
msgFromServer = "Hello UDP Client" bytesToSend = str.encode(msgFromServer)
# Create a datagram socket UDPServerSocket = socket.socket(family=socket.AF_INET, type=socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# Bind to address and ip UDPServerSocket.bind((localIP, localPort))
print("UDP server up and listening")
# Listen for incoming datagrams while(True): bytesAddressPair = UDPServerSocket.recvfrom(bufferSize) message = bytesAddressPair[0] address = bytesAddressPair[1] clientMsg = "Message from Client:{}".format(message)
# Sending a reply to client UDPServerSocket.sendto(bytesToSend, address) |
Output:
|
UDP server up and listening Message from Client:b"Hello UDP Server" Client IP Address:("127.0.0.1", 51696) |
Example: UDP Client using Python
|
import socket
msgFromClient = "Hello UDP Server" bytesToSend = str.encode(msgFromClient) serverAddressPort = ("127.0.0.1", 20001) bufferSize = 1024
# Create a UDP socket at client side UDPClientSocket = socket.socket(family=socket.AF_INET, type=socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# Send to server using created UDP socket UDPClientSocket.sendto(bytesToSend, serverAddressPort)
msgFromServer = UDPClientSocket.recvfrom(bufferSize)
msg = "Message from Server {}".format(msgFromServer[0]) print(msg) |
Output:
|
Message from Server b"Hello UDP Client" |
Applications of UDP:
-
UDP is used in DNS (Domain Name Service) queries. DNS queries are essential for Internet communication. As any domain name such as example.com is typed in the URL field of the browser these domain names are first translated to IP addresses before actual data transfer begins. The browser makes DNS queries primarily using UDP before opting for connection oriented protocols in case failures.
-
Other applications include SNMP, media streaming and VOIP. While transferring media like video or audio each has its own level of threshold of acceptable quality where pocket losses are tolerated.