Overview:
- Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) is computed as the mean of absolute deviation of data points from their mean.
- pandas DataFrame class has the method mad() that computes the Mean Absolute Deviation for rows or columns of a pandas DataFrame object.
- When mad() is invoked with axis = 0, the Mean Absolute Deviation is calculated for the columns. When axis=1, MAD is calculated for the rows.
- NaN values can be skipped using the optional Boolean parameter skipna. skipna=True skips the NaN values. skipna=False includes the NaN values. The default value for skipna is True.
Example 1:
|
import pandas as pd
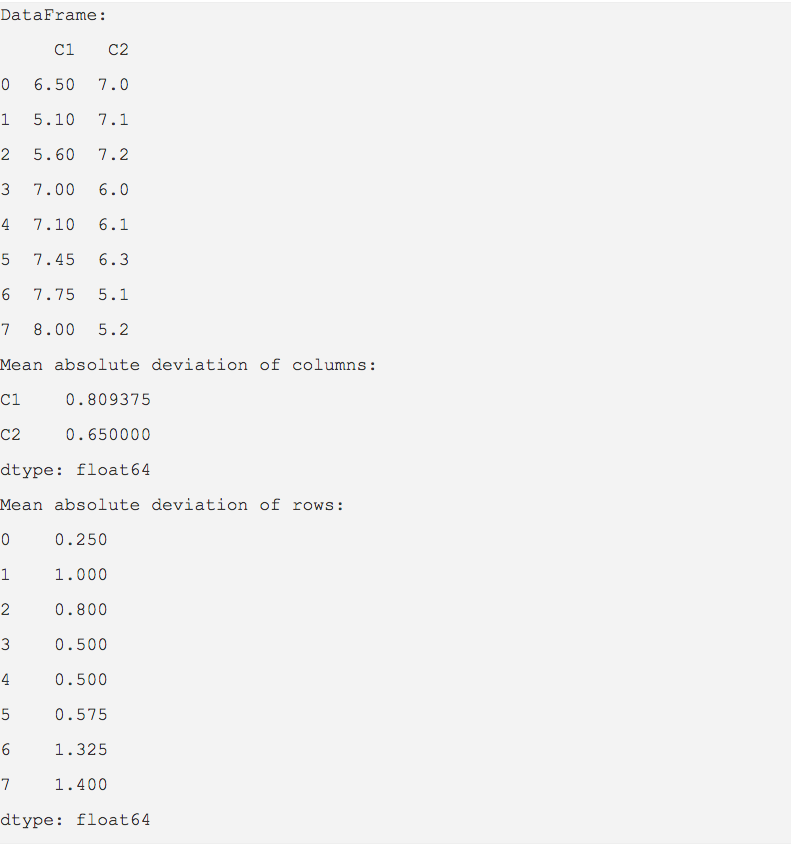
dataSet = {"C1":(6.5, 5.1, 5.6, 7.0, 7.1, 7.45, 7.75, 8), "C2":(7, 7.1, 7.2, 6, 6.1, 6.3, 5.1, 5.2) } dataFrame = pd.DataFrame(data=dataSet); print("DataFrame:"); print(dataFrame)
# Calculate Mean Absolute Deviation of DataFrame columns mad = dataFrame.mad(); print("Mean absolute deviation of columns:"); print(mad);
# Calculate Mean Absolute Deviation of DataFrame rows mad = dataFrame.mad(axis=1); print("Mean absolute deviation of rows:"); print(mad); |
Output:
Example 2:
|
import pandas as pd
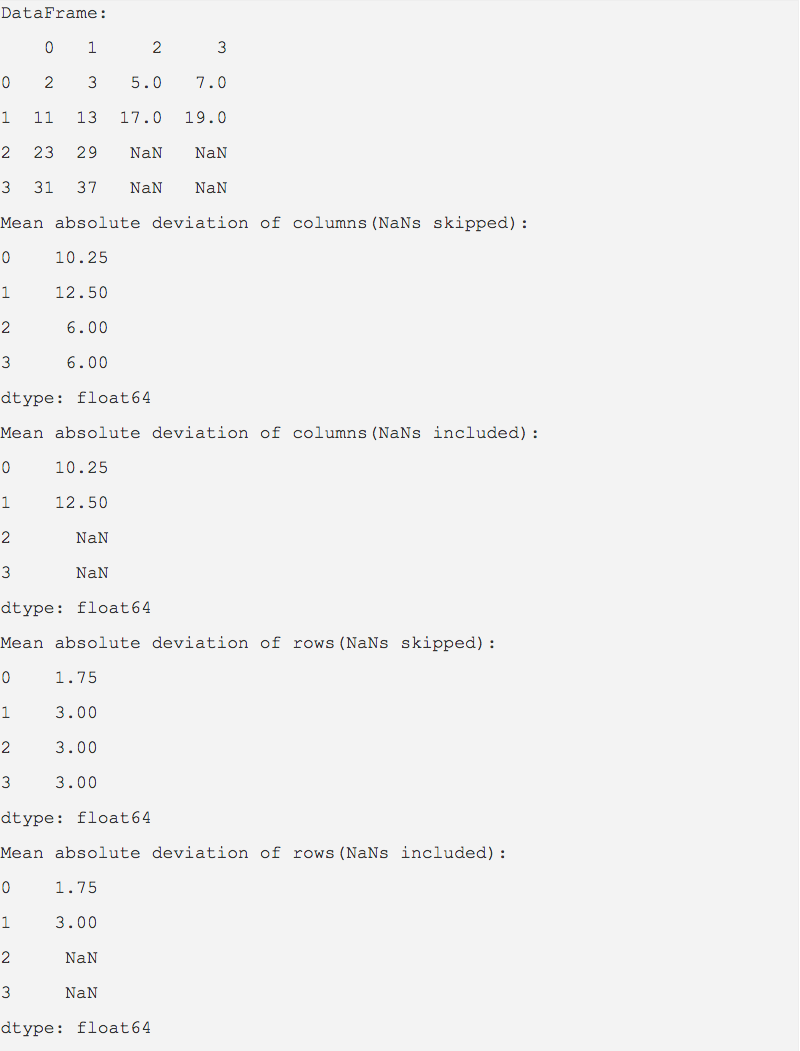
dataValues = [(2, 3, 5, 7,), (11, 13, 17, 19), (23, 29, None, None), (31, 37, None, None)]
dataFrameOject = pd.DataFrame(data=dataValues); print("DataFrame:"); print(dataFrameOject)
# Calculate MAD for the DataFrame columns mad = dataFrameOject.mad(axis=0); print("Mean absolute deviation of columns(NaNs skipped):"); print(mad);
# Calculate MAD for the DataFrame columns mad = dataFrameOject.mad(axis=0, skipna=False); print("Mean absolute deviation of columns(NaNs included):"); print(mad);
# Calculate MAD for the DataFrame rows mad = dataFrameOject.mad(axis=1); print("Mean absolute deviation of rows(NaNs skipped):"); print(mad);
# Calculate MAD for the DataFrame rows mad = dataFrameOject.mad(axis=1, skipna=False); print("Mean absolute deviation of rows(NaNs included):"); print(mad); |
Output: