Overview:
The Skewness is a measure of asymmetry of a probability distribution. Another measure that describes the shape of a distribution is kurtosis. In a normal distribution, the mean divides the curve symmetrically into two equal parts at the median and the value of skewness is zero. When a distribution is asymmetrical the tail of the distribution is skewed to one side - to the right or to the left.
Negatively skewed distribution:
When the value of the skewness is negative, the tail of the distribution is longer towards the left hand side of the curve. The test scores from example 1 are negatively skewed, resulting in a distribution having long tail to the left of the distribution as given in the output below.
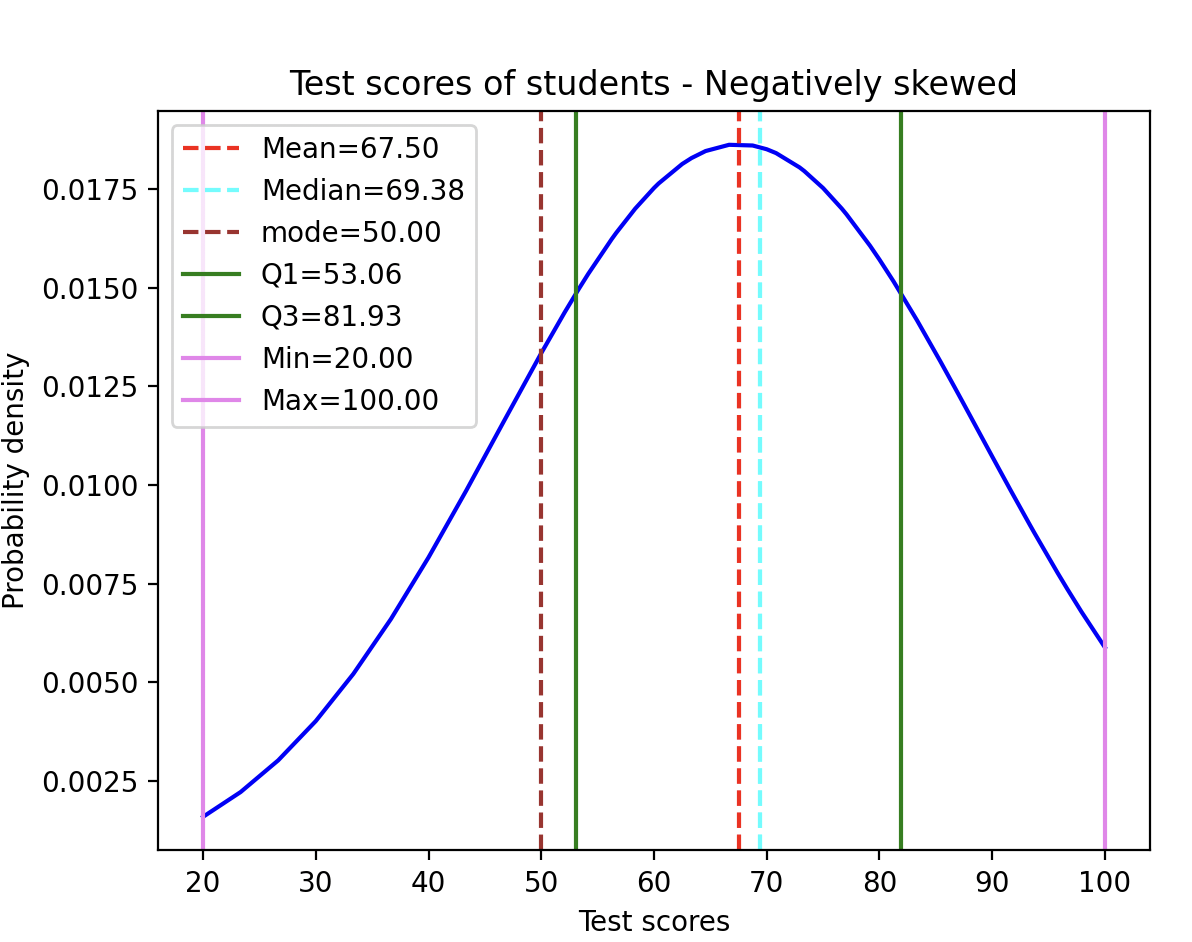
Unlike a symmetrical normal distribution where the mean, median and mode are all equal, these measures are unequal in a negatively skewed distribution. As a result, the mode (most frequent value of the distribution) is the highest, followed by the median (the middle value), and the mean (the average) is the lowest (Mean < Median <Mode). While this is typical of a negatively skewed distribution, in the example below containing test scores the relationship observed is Mode < Mean <median.
The observations loaded into the pandas DataFrame provides a skewness value of -0.416704 for the distribution.
Positively skewed distribution:
When the value of the skewness is positive, the tail of the distribution is longer towards the right hand side of the curve. The Python example 2 produces a distribution which is skewed to the right side. It plots the price of an asset over time using normal distribution with the help of the matplotlib library and the stats module of scipy. The output from matplotlib is given below:
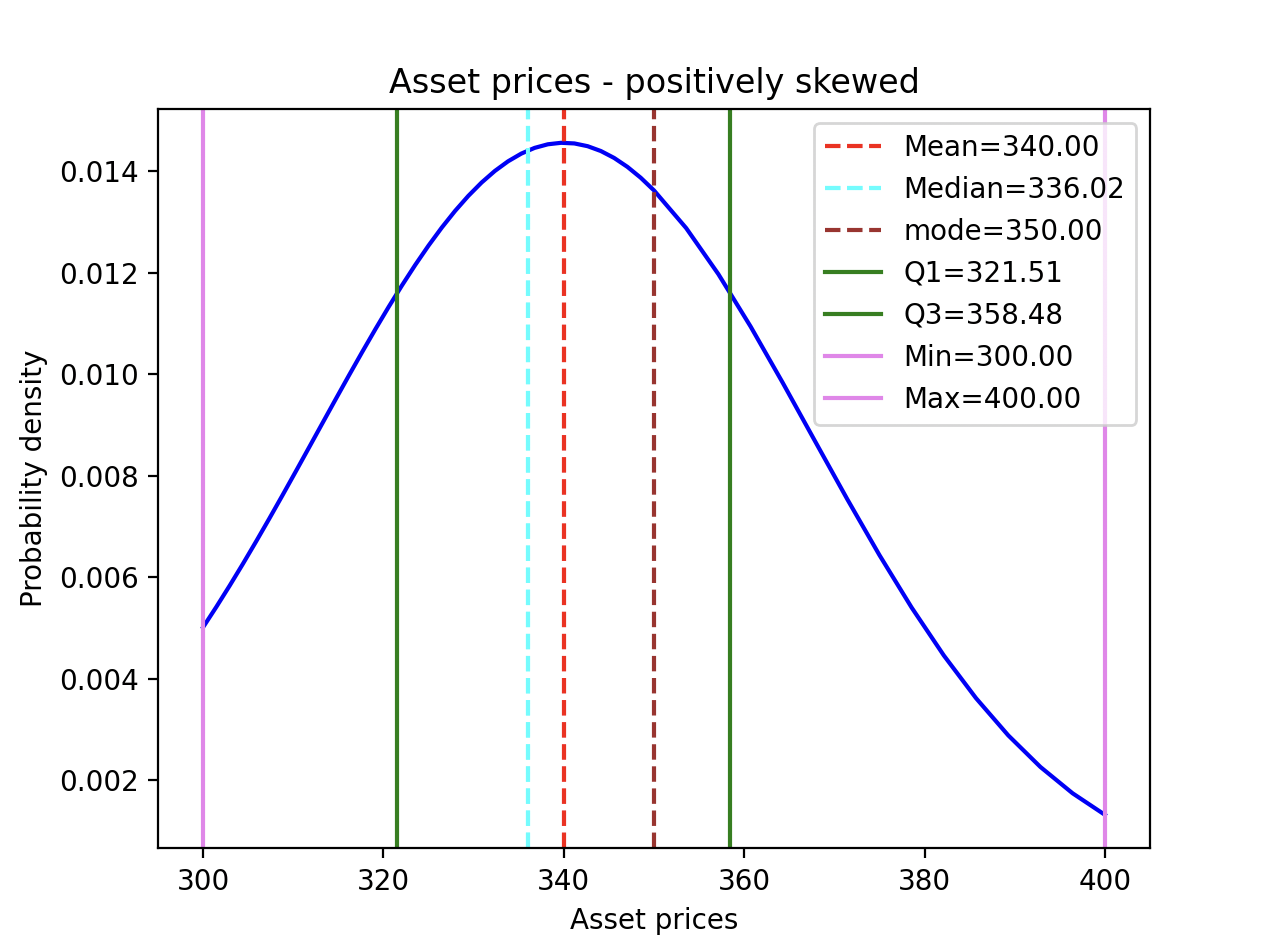
The skewness() function in pandas:
- The DataFrame class of pandas has a method skew() that computes the skewness of the data present in a given axis of the DataFrame object.
- Skewness is computed for each row or each column of the data present in the DataFrame object.
Example 1 - Negatively skewed distribution:
|
# Example Python program that plots a set of points # Test scores of 50 students dataFrame = pds.DataFrame(testScores) # Find measures of central tendency print("Mean:{:.2f}".format(mean)) # Find standard deviation # Analysis of quartiles q1Count = ((testScores <= firstQuartile) & (testScores >= min)).sum() q2Count = ((testScores <= mean) & (testScores >= firstQuartile)).sum() q3Count = ((testScores <= thirdQuartile) & (testScores >= mean)).sum() q4Count = (testScores >= thirdQuartile).sum() # Compute Y values using normal distribution # Plot the distribution # Give a title # Display the plot |
Output:
| Skew: 0 -0.416704 dtype: float64 Mean:67.50 Median:69.38 Mode:50.00 Mode count:2.00 Standard deviation:21.40 Scores in the first quartile: 12 Scores between first quartile and mean: 12 Scores between mean and third quartile: 11 Scores beyond third quartile: 15 |
Example 2:
|
# Example Python program that plots a set of points assetPrices = [300.0, 301.47, 302.94, 304.41, 305.88, # Find the value of skewness # Find measures of central tendency print("Mean:{:.2f}".format(meanValue)) # Find standard deviation # Analysis of quartiles q1Frequency = ((assetPrices <= quartileOne) & (assetPrices >= min)).sum() q2Frequency = ((assetPrices <= meanValue) & (assetPrices >= quartileOne)).sum() q3Frequency = ((assetPrices <= quartileThree) & (assetPrices >= meanValue)).sum() q4Frequency = (assetPrices >= quartileThree).sum() # Compute Y values using normal distribution # Plot the distribution # Give a title # Display the plot |
Output:
|
Skew |
Example 3:
|
import pandas as pd
dataVal = [(10,20,30,40,50,60,70), (10,10,40,40,50,60,70), (10,20,30,50,50,60,80)] dataFrame = pd.DataFrame(data=dataVal); skewValue = dataFrame.skew(axis=1)
print("DataFrame:") print(dataFrame)
print("Skew:") print(skewValue) |
Output:
|
DataFrame: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 1 10 10 40 40 50 60 70 2 10 20 30 50 50 60 80 Skew: 0 0.000000 1 -0.340998 2 0.121467 dtype: float64 |
- A skewness value of 0 in the output denotes a symmetrical distribution of values in row 1.
- A negative skewness value in the output indicates an asymmetry in the distribution corresponding to row 2 and the tail is larger towards the left hand side of the distribution.
- A positive skewness value in the output indicates an asymmetry in the distribution corresponding to row 3 and the tail is larger towards the right hand side of the distribution.