Overview:
- A digital image is a two-dimensional plane of pixels and it has a width and height.
- The Image class in Pillow has an attribute size. This tuple has the width and height of the image as its elements.
- An image can be resized to a given width and height using the resize() method of Pillow’s Image class.
- The resized image can be saved to disk by calling the save() method on image object of the resized image.
- Resampling is applied to all the pixels that could affect the outcome. The available resampling methods are: NEAREST, BOX, BILINEAR, HAMMING, BICUBIC, LANCZOS.
- The resize() method has the NEAREST filter as the default resampling method.
- A rectangle region can as well be specified within the available image size, which will be scaled and displayed as a new Image.
Example 1 – Resize and save the resized image using Python and Pillow:
|
# ----- Example Python program to resize an Image ----- from PIL import Image
# Create an Image object from a jpg file img = Image.open("whale.jpg");
# Make the new image half the width and half the height of the original image resizedImage = img.resize((round(img.size[0]*.5), round(img.size[1]*.5)));
# Display the original image img.show();
# Display the resized image resizedImage.show();
# Save the resized image to disk resizedImage.save("whale_resized.jpg");
# Scale a region resizedAndScaled = img.resize((round(img.size[0]*.5), round(img.size[1]*.5)), box=(100,100,200,225)); resizedAndScaled.show(); |
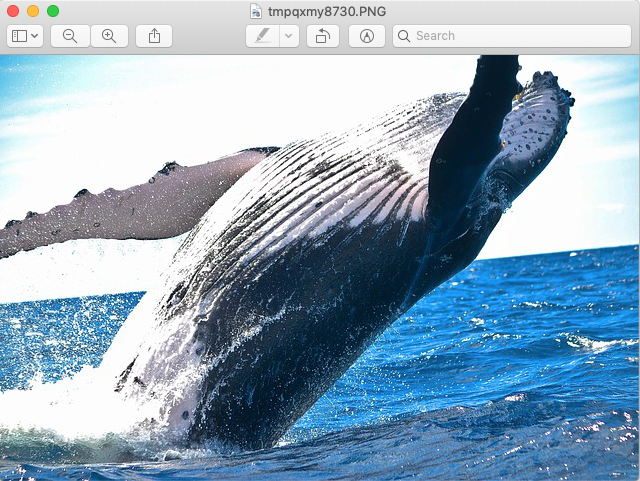
Original Image:
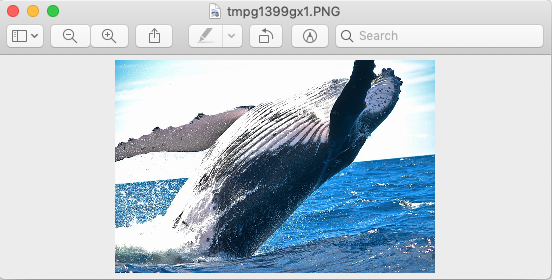
After resizing using Python and Pillow:
After resizing and scaling using Python and Pillow:
