Overview:
- Many of the images acquired, be it photographs or medical images from modalities like CT, MR, NM often require certain image enhancements for viewing the details hidden in the images through normal eyes.
- Contrast stretching or Normalization is one such operation applied on images, which improves the contrast of the image so that the details present in the image can be clearly seen.
Point operation on spatial domain:
-
Contrast stretching is applied directly on the image by modifying each pixel present in the image - that is by applying point operations rather then using a kernel.
-
By not using a kernel means each pixel value is not determined using the values of a neighborhood pixels. The intensity value of the pixel is modified using a normalization formula.
-
Contrast stretching is applied directly on the image, it does not involve converting an image to some intermediate form and finally applying an inverse transform to get the image back.
-
Contrast stretching of an image modifies the pixel values of the image in such a way that the intensities are transformed into a bigger range.
-
Contrast stretching is a linear operation which means the value of the new pixel linearly varies based on the value of original pixel.
-
A contrast-enhanced image can be converted back to the original image, as the transformation applied is linear.
-
Contrast stretching maps one intensity range present in the image to another intensity range.
-
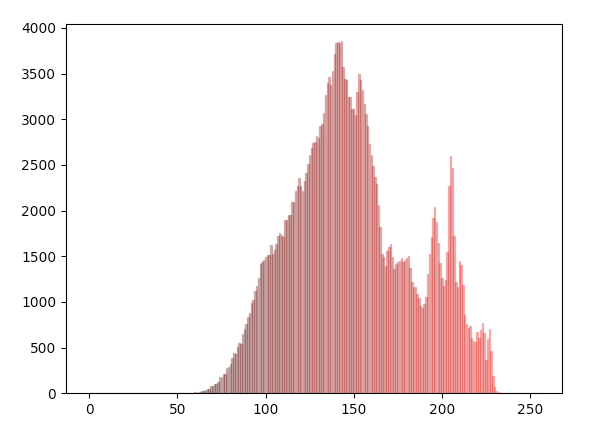
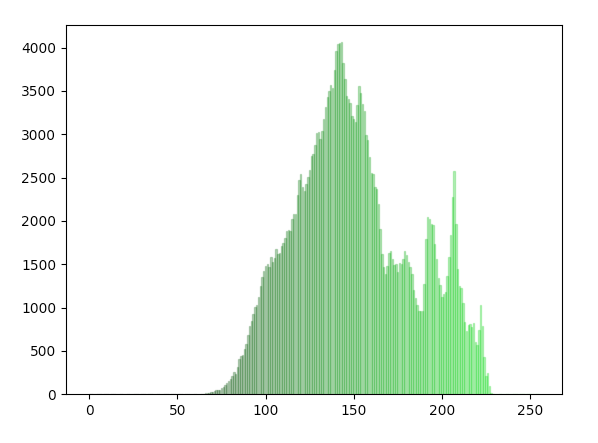
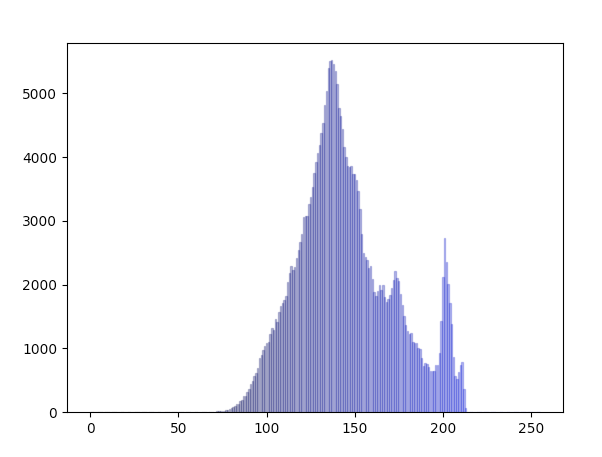
The new intensity range should be selected using the histogram of an Image so that the minimum intensity and the maximum intensity values present in the image are carefully selected excluding the outliers.
The Formula for Contrast stretch or Image Normalization
Io = (Ii-Mini)*(((Maxo-Mino)/(Maxi-Mini))+Mino)
Io - Output pixel value
Ii - Input pixel value
Mini - Minimum pixel value in the input image
Maxi - Maximum pixel value in the input image
Mino - Minimum pixel value in the output image
Maxo - Maximum pixel value in the output image
Contrast stretch using Python and Pillow:
- The Python Image Processing Library supports point image operations through method point()of the Image module.
- The point()method takes a function as a parameter. The function passed in accepts one argument and typically this is the pixel value that is to be transformed.
- In case of contrast stretching of an image, the formula for contrast stretching can be implemented inside a function, which takes the pixel value as a parameter and returns the modified intensity of the pixel.
Example:
|
# Example Python Program for contrast stretching from PIL import Image
# Method to process the red band of the image def normalizeRed(intensity): iI = intensity
minI = 86 maxI = 230
minO = 0 maxO = 255
iO = (iI-minI)*(((maxO-minO)/(maxI-minI))+minO) return iO
# Method to process the green band of the image def normalizeGreen(intensity): iI = intensity
minI = 90 maxI = 225
minO = 0 maxO = 255
iO = (iI-minI)*(((maxO-minO)/(maxI-minI))+minO) return iO
# Method to process the blue band of the image def normalizeBlue(intensity): iI = intensity
minI = 100 maxI = 210
minO = 0 maxO = 255
iO = (iI-minI)*(((maxO-minO)/(maxI-minI))+minO) return iO
# Create an image object imageObject = Image.open("./glare4.jpg")
# Split the red, green and blue bands from the Image multiBands = imageObject.split()
# Apply point operations that does contrast stretching on each color band normalizedRedBand = multiBands[0].point(normalizeRed) normalizedGreenBand = multiBands[1].point(normalizeGreen) normalizedBlueBand = multiBands[2].point(normalizeBlue)
# Create a new image from the contrast stretched red, green and blue brands normalizedImage = Image.merge("RGB", (normalizedRedBand, normalizedGreenBand, normalizedBlueBand))
# Display the image before contrast stretching imageObject.show()
# Display the image after contrast stretching normalizedImage.show() |
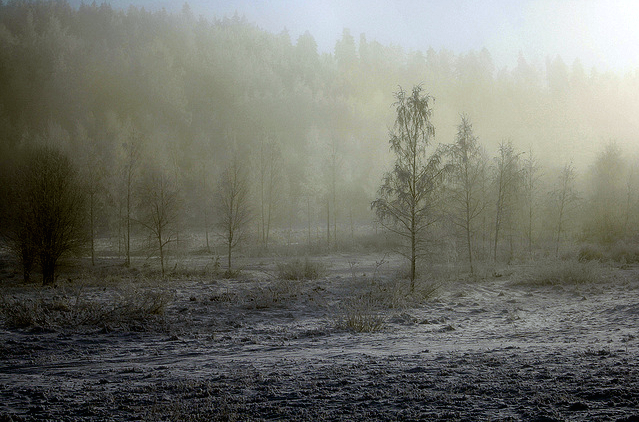
Input Image for Contrast Stretching Operation:

Courtesy: Miguel Virkkunen Carvalho
Histogram of the Input Image(Helps in defining the intensity range):
Red Band of the Image:
Green Band of the Image:
Blue Band of the Image:
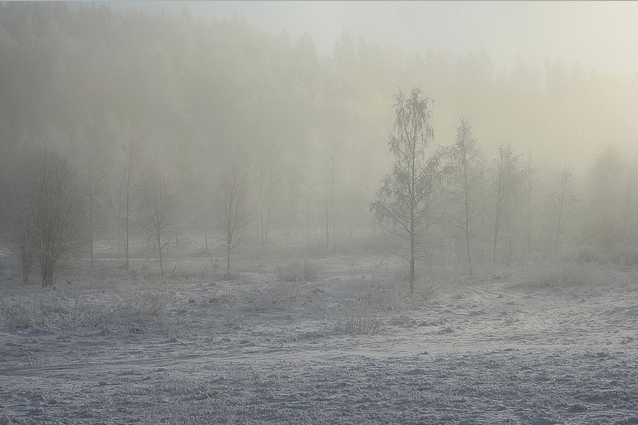
Output Image after applying contrast stretching: